Using Block Chain to Extend Your Processes Beyond the Enterprise
For many decades now Business Process Management has been a technology that has helped organizations become more efficient. For several years now BPM has been helping banks, financial service companies, insurance companies and other businesses streamline their processes through the use of workflows.
The question of extending processes beyond the boundaries of an organisation is tricky one. Each partner to a multi-entity process will have their own systems and will not be willing to abandon these systems to use a partner platform.
This is where block chain can add value. Block Chain will allow each business partner to retain their system for internal processing and publish shared information such as contracts or legal documents to a common trusted network.
By using systems which are Block Chain compatible or can write to the block chain, enterprises can extend their BPM beyond the boundary of the business.
eDGEVANTAGE provides integrated workflow, document management and decision support functionality
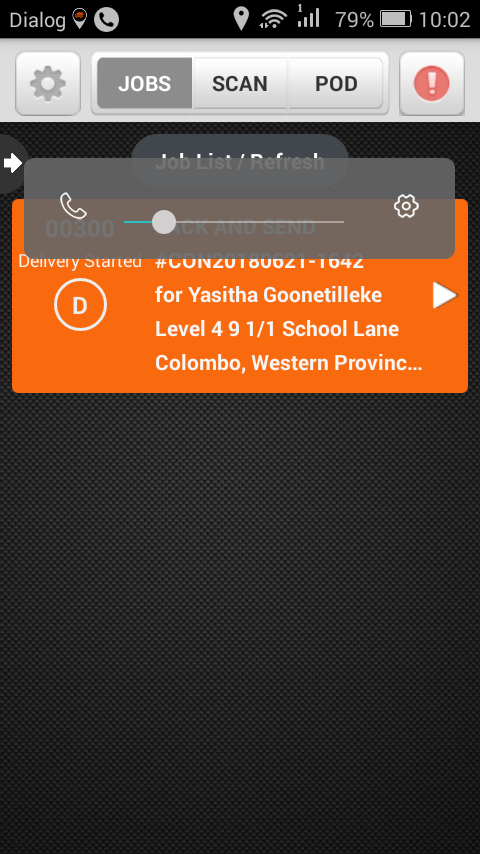
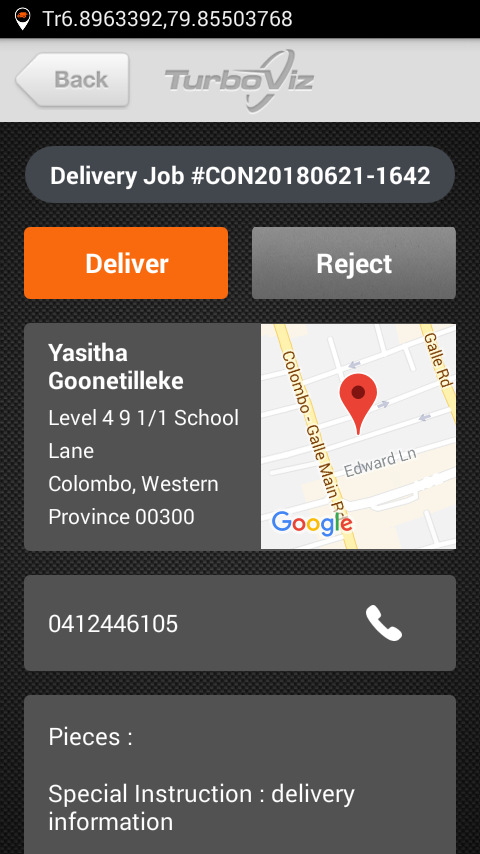
Mobile Apps Used with eDGEVANTAGE
Business Process Management via eDGEVANTAGE
BPM is a Digital Automation Framework that helps organizations improve overall efficiency and the ability to execute consistently. It streamlines business processes within an organization where participants normally trust each other. Innovations in areas such as Case Management, Event Processing, Business Rules, and Integration Mechanisms help organizations address strategic goals by implementing new and continuously improving existing business processes.
There are BPM platforms such as eDGEVANTAGE, which provide integrated Workflow, Document Management and Decision Support Functionality. Where most of the functionality around a process is also built within the platform. Giving customers BPM and much more.
Most eDGEVANTAGE solutions contain more than just basic process management functionality. In addition to the basic process, all checklists are digitized into the platform, and are used as logic in routing the workflow. All documents which are an essential part of the process are attached within the task and form the framework. In addition the system is integrated to other legacy systems to either collect or write our data to and from these systems. All data required for decision making is presented in an easy to use graphical format, within the task forms, so that the relevant user has all required data in order to make an informed decision
In instances when processes start off outside the company’s boundaries, or when confirmation of service delivery takes place outside the boundary of the enterprise, mobile applications are used to extend the use of the workflow outside of the business premises.
The Challenge of Extending Processes Beyond the Enterprise
In real life scenarios, business processes rely on data from information systems outside their control, even data from other enterprises. This data must move between organizations, or even between enterprises, which is not only complex and expensive but often results in stale and inconsistent data. Lack of transparency and trust is the consequence.
When a process needs to be extended beyond the boundaries of one enterprise to other partner enterprises, there are usually a plethora of hard copy documents involved, and an army of resources are deployed to check and verify documents received in order to validate and process same.
- In tourism the voucher as a document between the DMC and the hotel, or the booking confirmation between an agent and the DMC.
- In procurement the exchange of Purchase Orders, Good Receipt Notes, and Invoices are an example of such documents.
- In banking a request for a Credit Rating Report (CRIB) or a confirmation to make payments on behalf of a client
- A claim intimation, a repair estimate, a repairs bill and the insurance settlement in an Insurance claims process
The reasons for this include the need of each partner to protect the integrity of their own system. To ensure a due diligence is done by each party to ensure they have satisfied themselves that the request received for processing is genuine. To run efficiently, business processes rely on data from information systems. However, what happens when data is created and modified in information systems outside of an organization? A common procedure today is moving the data that processes need between fragmented information systems. This approach is complex and expensive and often results in outdated and inconsistent data. And more concerning, lack of transparency and trust is the consequence.
The basic assumption being that any system which is not under direct control of the enterprise is not a trusted application and therefore any request received from these systems must be verified and authenticated
In some instances many businesses who are partner to a single process will integrate their own systems to one another, via web-services. But there are limitations to the level of access provided and each partner needs to be integrated to each of the others. The integrations cannot be easily replicated to a separate business group without incurring specific development and integration costs. The lack of a common de-centralized, peer-to-peer network is therefore the main issue that will not allow different enterprises to connect seamlessly.
However, if the business network includes a distributed ledger that maintains a single version of the truth, the ledger provides the interface. Participants retrieve and update information on the ledger and react to events when information is updated by others. By using a distributed ledger as the underlying system of records, all participants can achieve significant business process improvements.
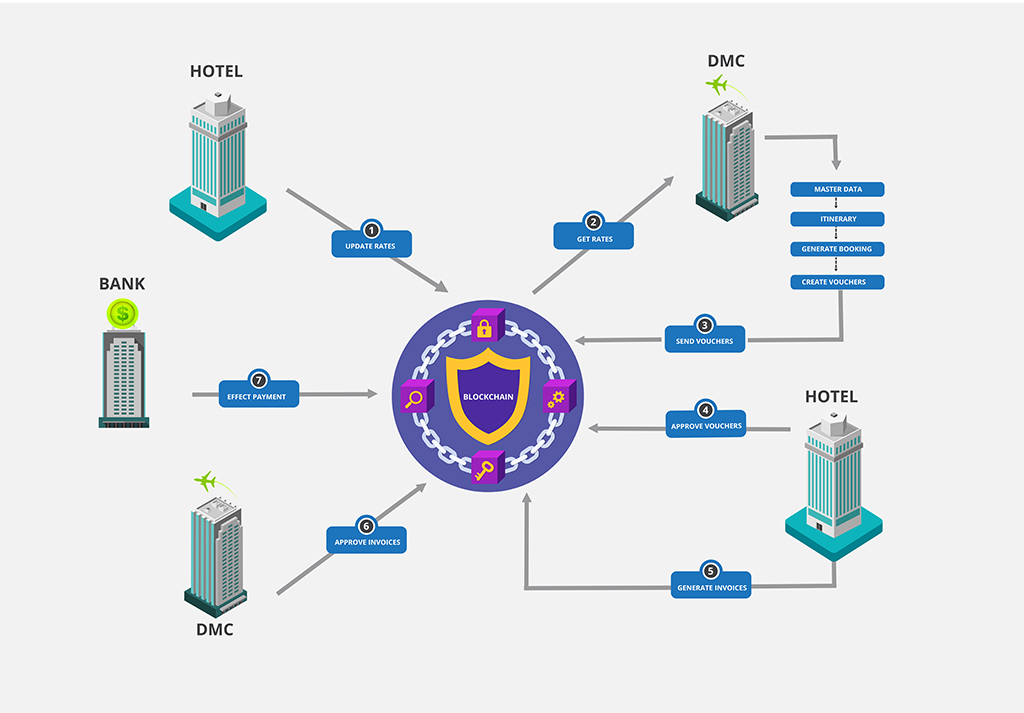
A Block Chain Example in Tourism
Let’s look at an example in the Tourism Industry which includes a hotel, a DMC and a bank:
- A hotel would create its rates for all room types at a particular property, (inclusive of special offers, shoulder rates) and store it on the block chain
- The DMC retrieves the rates Block and identifies different rates made available for it and uses them to create itineraries
- When a created itinerary is sold the DMC confirms the date, room types, number of rooms and guest details by invoking a transaction on the Blockchain and generating a voucher
- Once the stay is done the hotel can write the invoice to the Blockchain
- The DMC would then review and confirm the payment to the Blockchain
- The bank would then invoke a transaction to pay the hotel for services rendered
Even today this use case can be recreated using EDI and web-services to facilitate a hotel to speak to a DMC system to system
The issue is that you would need a different integration for every hotel the DMC wants to connect to. This is both time and effort intensive and costly
With Blockchain the cost is minimal since each party to the transaction must have systems with the ability to write to and execute transactions on the Blockchain
Enter Block Chain!
Blockchain enables the execution of Business Processes across multiple organizations and distrusted participants.
Blockchain is widely accepted as an answer to Trust and Transparency issues in business networks that span organizations for the following reasons:
Participants in the network use a shared ledger to perform transactions on assets.
Transactions are validated by participants through a consensus protocol.
Smart contracts control transactions between participants, which therefore do not need to trust each other. Smart contracts ensure that contractual conditions are met, and obligations are enforced.
Permissive Blockchains ensure that all information and transactions on the Blockchain are available only to Network members with the right permission.
Therefore Blockchain technology can be an answer to Interoperability, Trust, and Transparency issues in fragmented systems. At its core, Blockchain is a distributed system that captures details of asset and transaction records. Smart contracts control the execution of transactions between distrusted parties and ensure that contractual conditions are met, and obligations are enforced. Permissioned Blockchains ensure that all information and transactions on the Blockchain are available only to network members with the right permission.
BPM & Block Chain
In a combined solution, the shared ledger provides the interface for different business processes to meet and exchange information. A process queries asset information and performs transactions directly on the ledger. Therefore stale or inconsistent data is a thing of the past! In addition, business events on the Blockchain initiate or drive business processes, ensuring that the right organizations are involved and react to events in a timely manner. The combination of both business process management and Blockchain helps you to reach the next level of integration and automation of business processes. You can significantly improve your business processes using a BPM engine that can write to the Blockchain.